Introduction
The integration of technology, satellites, and data management into agriculture has opened up exciting possibilities for the future, especially in the context of sustainable agriculture. In the face of a growing global population and the challenges posed by climate change, agriculture is undergoing a transformative journey. One of the most promising trends in this evolution is the fusion of technology and satellite data with farming practices, enabling farmers to manage their operations more efficiently, enhance productivity, and contribute to the overarching goal of sustainable agriculture.
In the pursuit of sustainable agriculture, technology has emerged as a game-changer. One of the key challenges faced by farmers is the need to maintain a balance between maximizing yields and minimising environmental impact. Farmers have to continually measure, analyse, assess and adapt to various components of their farming system in order to determine whether they are indeed managing their farm in an efficient and sustainable manner. This is precisely where technology and data steps in, offering a range of tools and solutions that empowers farmers to make informed decisions while minimizing resource wastage.
Using data to achieve sustainable farming
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture leverages cutting-edge technologies such as GPS, sensors, and data analytics to enable farmers to optimize farming practices by adapting to the specific needs of individual fields. Precision agriculture utilizes real-time data which empowers farmers to make informed decisions. This is particularly crucial in the context of dairy farming, where soil health, nutrient management, and water usage plays a pivotal role in maintaining sustainable operations.
Satellite Technology: A Bird’s Eye View of Farms
Satellites have revolutionized our ability to monitor and manage farms from above. Satellites equipped with advanced imaging technology offer a comprehensive view of agricultural landscapes. They provide a unique vantage point, allowing farmers to assess various aspects, from crop health and growth to water distribution and soil moisture levels. This data can also reveal variations in the system thereby enabling farmers to address specific areas that need attention.
Tools for Soil Health Assessment and Management
Maintaining healthy soil is fundamental for sustainable agriculture. Technology-driven tools aid farmers in assessing soil health parameters. By recording these measurements over time, farmers can track trends and identify and rectify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach not only optimizes crop yields but also prevents soil degradation and promotes long-term sustainability.
Nutrient and Water Management
Efficient nutrient and water management are central to sustainable dairy farming. Technology offers real-time monitoring of nutrient levels and irrigation systems, ensuring that plants receive the right amount of nutrients and water without wastage. Accurate data collection and record-keeping enable farmers to fine-tune their practices, reducing environmental impact and improving resource efficiency.
Importance of keeping records
One of the cornerstones of sustainable agriculture is informed decision-making. Keeping meticulous records of management practices and their outcomes plays a critical role in this process. As the world places greater emphasis on environmental protection and sustainable practices, farmers are under increased pressure to comply with regulations. Technology-driven record-keeping simplifies the process of documenting and reporting farming practices, ensuring transparency and accountability. It is therefore vital to keep records for the following reasons:
- Historical Insights: Detailed records provide a historical perspective on crop performance, enabling farmers to identify trends and patterns. This retrospective analysis aids in adjusting strategies for better outcomes.
- Accountability: In an era where consumers are increasingly interested in the origin of their food and its production methods, transparent record-keeping demonstrates a commitment to ethical and sustainable practices.
- Compliance and Certification: Sustainable agriculture often requires adherence to specific regulations and certifications. Accurate records make it easier to demonstrate compliance and maintain certification status.
- Continuous Improvement: Records act as a foundation for continuous improvement. By identifying what works and what doesn’t, farmers can refine their practices, ultimately boosting productivity and sustainability.
Trace & Save wants to support you in your data-driven management journey
Trace & Save sustainable measures, assessments and the Trace & Save database
The Trace & Save system, which has data-driven management at the centre of it, uses multiple measures of on-farm indicators to attain a trustworthy, holistic measure of agricultural sustainability.
“Trace & Save aims to help farmers identify opportunities to improve farm management, provide farmers with insight as to how the sustainability of their farm is improving relative to their own baseline, show agri-processing companies whether farmers are improving the sustainability of their food production and show consumers how farmers are becoming more sustainable” (Trace and Save Technical Document).
Trace & Save uses the SWAN system to measure and assess on-farm sustainable practices. The SWAN system incorporates measures of the following aspects:
- Soil and soil health management, assessing soil life, fertility and structure
- Water and water management, which assess soil water holding capacity, water use efficiency, effluent management and the protection of freshwater resources
- The atmosphere, which encompasses the assessment of greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon footprint assessments and an indication of carbon sequestration and carbon neutrality
- Nutrients and nutrient management, which assesses mineral balances, nutrient cycling and feed energy flows on farms.
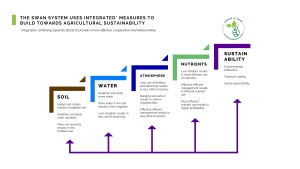
Figure 1: Diagram showing how the SWAN system supports sustainable agriculture.
The measuring and assessment of this data equips farmers with a comprehensive tool for sustainable decision making and management. By capturing data each year, farmers further build a record from which they can gain historical farm insights. Equally as important, it provides the farmer with evidence of the farming operation, which is becoming more and more important in a world where there are pressures for emission reductions and more sustainable practices.
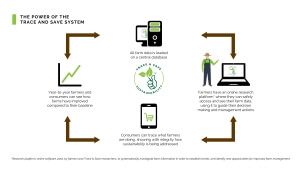 Figure 2: Diagram showing the power of, and illustrating what differentiates, the Trace & Save system.
Figure 2: Diagram showing the power of, and illustrating what differentiates, the Trace & Save system.
The Trace & Save database, which consists of multiple years of data across multiple farms, further allows the Trace & Save research team to provide farmers with current and insightful research, further supporting decision making.
SPS app as an on-farm daily management tool
 Trace & Save have recently developed a mobile app, called SPS (Sustainable Precision System). The aim of this app is to support farmers with day-to-day farm management.
Trace & Save have recently developed a mobile app, called SPS (Sustainable Precision System). The aim of this app is to support farmers with day-to-day farm management.
The app links to Fourth Quadrant, the Trace & Save database and has the ability to link to different APIs. APIs allows the app to pull data from other data collection systems, such as weather and satellite data.
Using the various data sources, the app has the capability to show various reports, including:
- The pasture biomass per camp
- Weekly pasture biomass reports per farm
- Soil results per camp
- Irrigation reports
- Pasture back calculations
The app also allows for users to capture data in real time, including:
- Pasture walks
- Grazing events
- Team data
- Irrigation and rainfall data
- General notes per camp
The use of the SPS app therefore is an all-encompassing tool supporting daily management – all in the palm of your hand! By incorporating the use of precision systems and with multiple data integration, the app allows the user to obtain camp specific insights, supporting precision agriculture, efficient grazing management and optimal water and nutrient management.
Conclusion
The future of agriculture lies in the hands of those who embrace technology and innovation. For sustainable dairy farming, this means leveraging data, satellite insights, and advanced tools to optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and protect the environment. Equally as important is the practice of diligent record-keeping, which provides a roadmap for informed decision-making and ongoing improvement. By combining traditional wisdom with cutting-edge solutions, we can pave the way for a greener, more prosperous agricultural landscape—one where farmers not only feed the world but also nurture the planet.
Contact a Trace & Save team member to help you get started on your data-driven management journey, or if you want further insight on the services we can offer you.
